Problem
There is an undirected tree with n nodes labeled from 0 to n - 1, and rooted at node 0. You are given a 2D integer array edges of length n - 1, where edges[i] = [aᵢ, bᵢ] indicates that there is an edge between nodes aᵢ and bᵢ in the tree.
A node is good if all the subtrees rooted at its children have the same size.
A subtree of
treeNameis a tree consisting of a node intreeNameand all of its descendants.
Return the number of good nodes in the given tree.
https://leetcode.cn/problems/count-the-number-of-good-nodes/
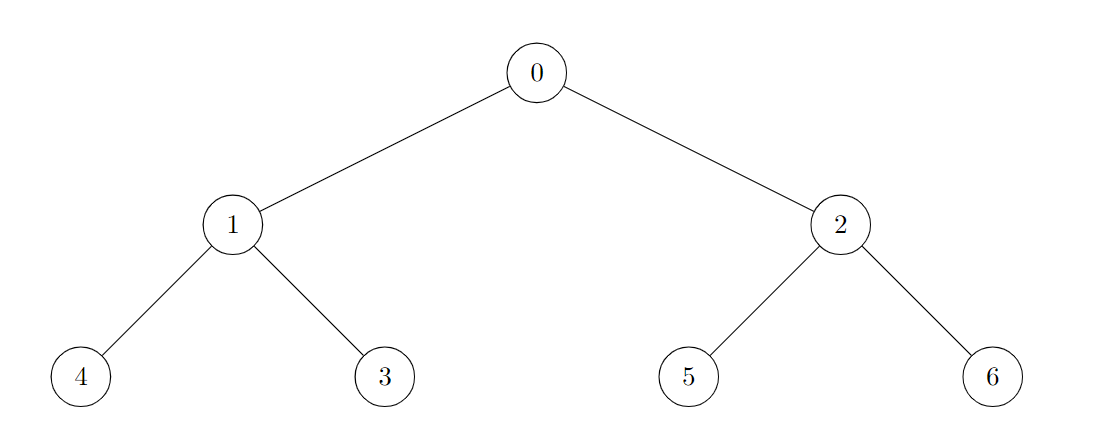
Example 1:
Input:
edges = [[0,1],[0,2],[1,3],[1,4],[2,5],[2,6]]
Output:7
Explanation:
All of the nodes of the given tree are good.
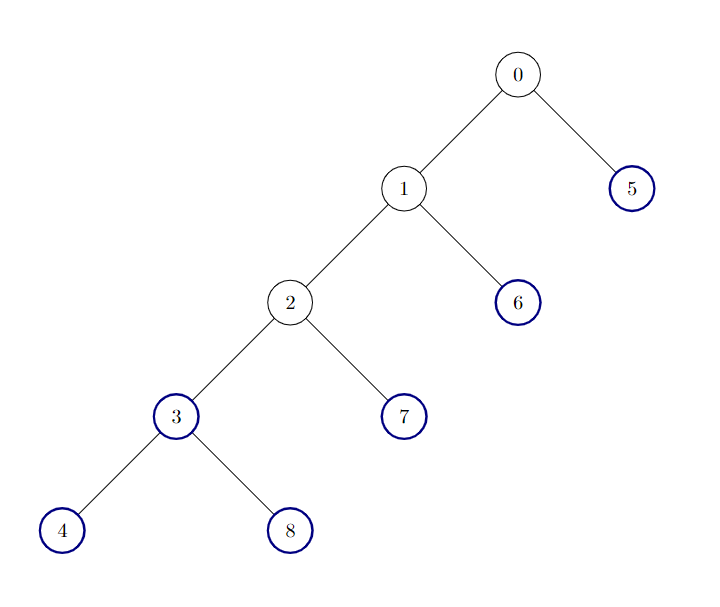
Example 2:
Input:
edges = [[0,1],[1,2],[2,3],[3,4],[0,5],[1,6],[2,7],[3,8]]
Output:6
Explanation:
There are 6 good nodes in the given tree. They are colored in the image above.
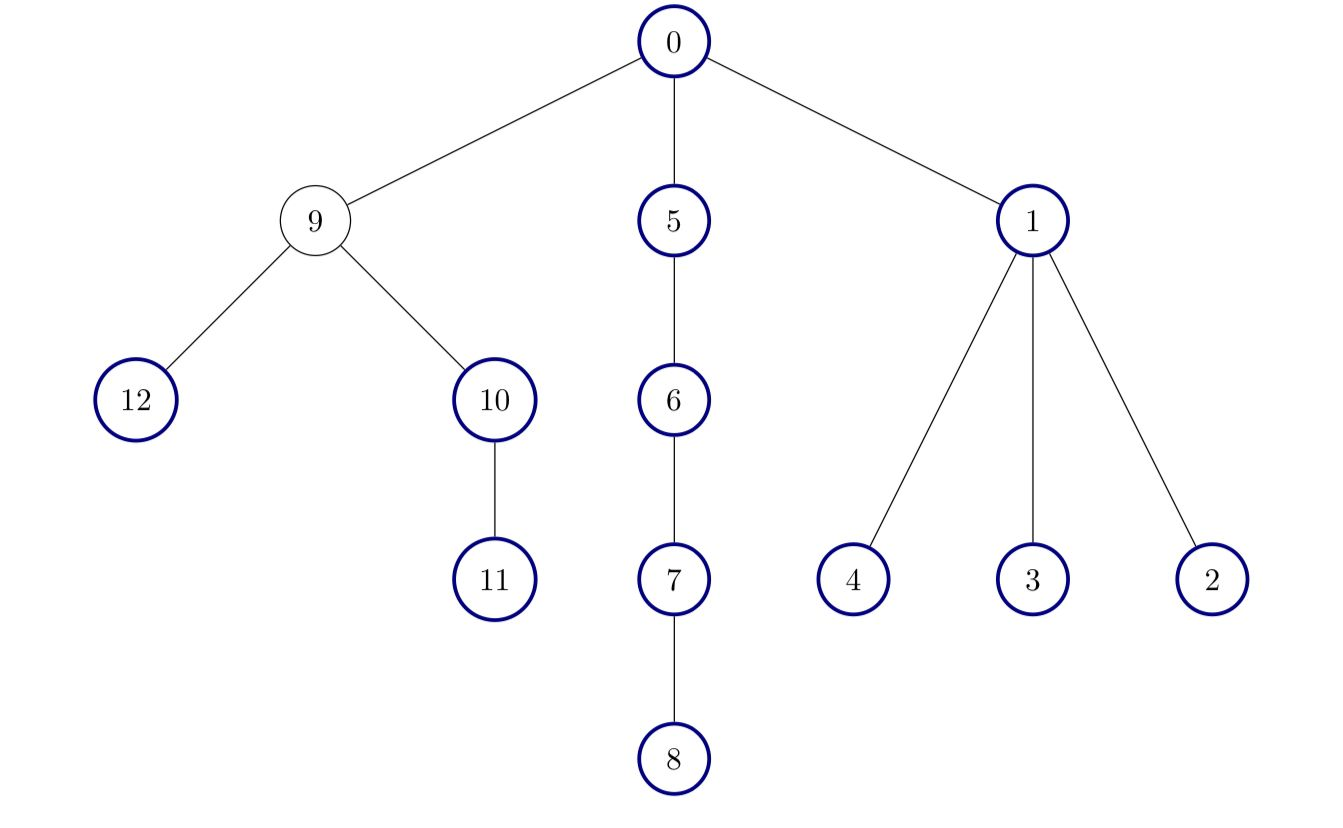
Example 3:
Input:
edges = [[0,1],[1,2],[1,3],[1,4],[0,5],[5,6],[6,7],[7,8],[0,9],[9,10],[9,12],[10,11]]
Output:12
Explanation:
All nodes except node 9 are good.
Constraints:
2 <= n <= 10⁵edges.length == n - 1edges[i].length == 20 <= aᵢ, bᵢ < n- The input is generated such that
edgesrepresents a valid tree.
Test Cases
1 | class Solution: |
1 | import pytest |
Thoughts
叶子节点显然是 good,以其为根的 subtree 的节点总数为 1,good 节点总数也是 1。
对于内部节点,先依次计算每个子节点 subtree 的节点总数和 good 节点总数。再根据这些信息判断当前节点是否 good,并累加得到以该节点为根的 subtree 的节点总数和 good 节点总数。
后序遍历整棵树,用栈避免递归调用。因为需要先处理完所有子节点之后再处理父节点,所以如果出栈的是一个尚未处理过内部节点,需要把该节点再次入栈(做适当标记),然后把所有子节点入栈,等子节点都计算完,再对该节点做收尾处理。
另外不用等所有子节点都处理完再判断父节点是否 good 以及累加其 subtree 的节点数和 good 节点数,可以在每处理完一个子节点(第二次出栈)时,就直接把相关信息更新到父节点上。一种方式是给每个节点都附加一份相关信息(节点总数、good 节点总数、是否 good、已知的子节点 subtree 的节点数量),另一种方式是只保留树根到当前节点通路上每个中间节点的信息,后者可以用另外一个栈辅助。
因为输入是边的集合,且不保证边中两个端点的顺序,需要先在内存中构建树。
对于每个节点,记录所有与其相连的边,包含其父节点和所有子节点。在后序遍历时,可以容易地排除掉父节点,只把所有子节点入栈。
需要 O(n) 空间辅助记录树的结构,O(n) 时间复杂度。
Code
1 | from typing import List |