Problem
There are n piles of coins on a table. Each pile consists of a positive number of coins of assorted denominations.
In one move, you can choose any coin on top of any pile, remove it, and add it to your wallet.
Given a list piles, where piles[i] is a list of integers denoting the composition of the iᵗʰ pile from top to bottom, and a positive integer k, return the maximum total value of coins you can have in your wallet if you choose exactly k coins optimally.
https://leetcode.cn/problems/maximum-value-of-k-coins-from-piles/
Example 1:
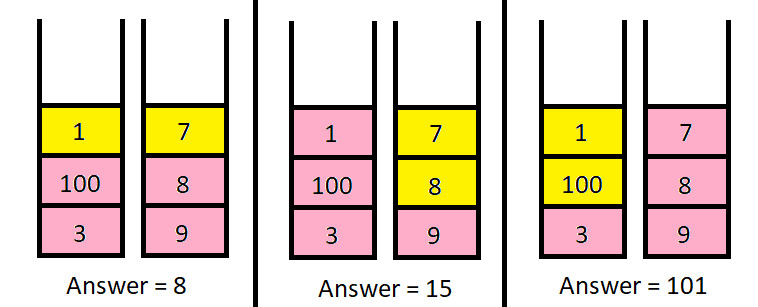
Input:
piles = [[1,100,3],[7,8,9]], k = 2
Output:101
Explanation:
The above diagram shows the different ways we can choose k coins.
The maximum total we can obtain is 101.
Example 2:
Input:
piles = [[100],[100],[100],[100],[100],[100],[1,1,1,1,1,1,700]], k = 7
Output:706
Explanation:
The maximum total can be obtained if we choose all coins from the last pile.
Constraints:
n == piles.length1 <= n <= 10001 <= piles[i][j] <= 10⁵1 <= k <= sum(piles[i].length) <= 2000
Test Cases
1 | class Solution: |
1 | import pytest |
Thoughts
记 dp(p, j) 表示从 piles[0...p] 中选取刚好 j 枚硬币(0 ≤ p < n,1 ≤ j ≤ k),可以得到的最大总额。
先不考虑边界情况(即假设每个 pile 都有足够多的硬币),显然有:
初值 dp(-1, j) = 0,dp(p, 0) = 0。最终结果为 dp(n-1, k)。
即从 piles[p] 取 i 枚硬币(0 ≤ i ≤ j),剩余的 j - i 枚从 piles[0...p-1] 取。
一个明显的优化是计算从 piles[p] 取 i 枚硬币的总额,并不需要对于所有的 i 都从 0 开始累加,只需要先计算一遍前缀和,然后直接利用 piles[p] 的空间存储前缀和。即更新后的 piles'[p][i] = Σpiles[p][0...i],可得:
计算 dp(p, j) 时只用到 dp(p-1, *),可以只保留最新的 p 对应的 dp 值。
时间复杂度 O(n * k²),空间复杂度 O(k)。
考虑到边界条件,可以有一些小优化。比如 piles[0...p] 包含的硬币总数比 k 小,则只需要计算到硬币总数,不需要计算到 k。如果 piles[p] 的硬币数大于 k,则只需要计算前 k 项的前缀和。对于任意 j,如果 piles[p] 的硬币数小于 j,则 这一项的上限可以只取到硬币数。
Code
1 | class Solution: |